20 Frequently Asked Questions in Data Governance
The significance of data governance is to help us discover data problems earlier, more timely, and more efficiently, and to ensure the quality, availability, integration, security, and ease of use of enterprise data.
Today, in this article, let’s take a look at 20 frequently asked questions in data governance.

Frequently Asked Questions in Data Governance
20 Frequently Asked Questions in Data Governance:
1. What is data governance?
Data governance is a strategic initiative to optimize the way an enterprise handles data. It is designed to organize and improve the policies and procedures that companies use to define, collect, store, protect, manage and monetize business data. Good data governance is not only about avoiding liability, but also about finding new ways to create value for the business.
2. What does data governance include?
Data governance involves organizations, systems, processes and information technology. It assesses and redefines roles and responsibilities, enhances policies to improve communication and sharing between departments, defines and expands access to business-critical data, and standardizes data collection and processing practices to ensure the quality and consistency of company data.
3. What is the business value of data governance?
Data governance helps companies avoid liability, save time and money on bad data, improve customer relationships, and actively generate revenue. With accessible, well-defined, and quality-controlled data, organizations are 23x more likely to acquire customers, 6x more likely to retain customers, and 19x more likely to be profitable.
4. Is data governance a program or a project?
Data governance is a long-term strategic business initiative, not a single short-term project. Implementing data governance requires structural changes to a company’s existing data policies and practices, as well as redefining the roles and responsibilities of data processors.
5. How can you help business managers understand the importance of a data governance program?
The best way to explain the importance of data governance to management is to focus on its benefits to the bottom line. Emphasize how data governance will advance company strategy and help achieve specific business goals. It is important to communicate that data governance is both about creating value and avoiding liability.
6. How to implement data governance?
The first step in implementing data governance is to have a clear understanding of your company’s corporate strategy. Identify specific business goals that can be achieved with data, and define the specific data elements required to achieve those goals. With all of this in mind, identify what improvements can be made to existing data and procedures and begin drafting new policies accordingly.
7. How to measure the success of data governance?
Measure the success of your data governance program by establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) ahead of time. Be sure to tie the KPIs to your organization’s specific corporate strategy and specific business goals. This will ensure success is measured in terms that are relevant to management and meaningful to the entire business.
A KPI might track an improvement in the quality of an enterprise’s data, an increase in the number of terms defined in a business glossary, or a decrease in the time spent searching, organizing, and cleaning data. Another way to demonstrate success is to document the improvement in an organization’s data management maturity level over time.
8. Why does data governance fail?
Data governance programs often fall apart when they fail to ensure business support. It is important to have a business sponsor who can ensure that business management and IT remain actively involved in the program. Data governance programs are also susceptible to overinfluence. It is important to establish reasonable short-term goals that are highly aligned with the company’s strategy.
9. What is the difference between data governance and data management?
Data governance broadly involves organizational strategies, policies, and procedures. It provides executive oversight and dictates how data should be processed to advance business objectives. In contrast, data management deals with the tools and practices used to process data and implement the strategies outlined in data governance.
10. What is a data owner?
Data owners are individuals who are ultimately responsible for the quality of one or more datasets. They are usually senior employees with the authority, budget, and resources to define, cleanse, and maintain the data they “own”. The data owner is usually not the same person responsible for the day-to-day management of the data.
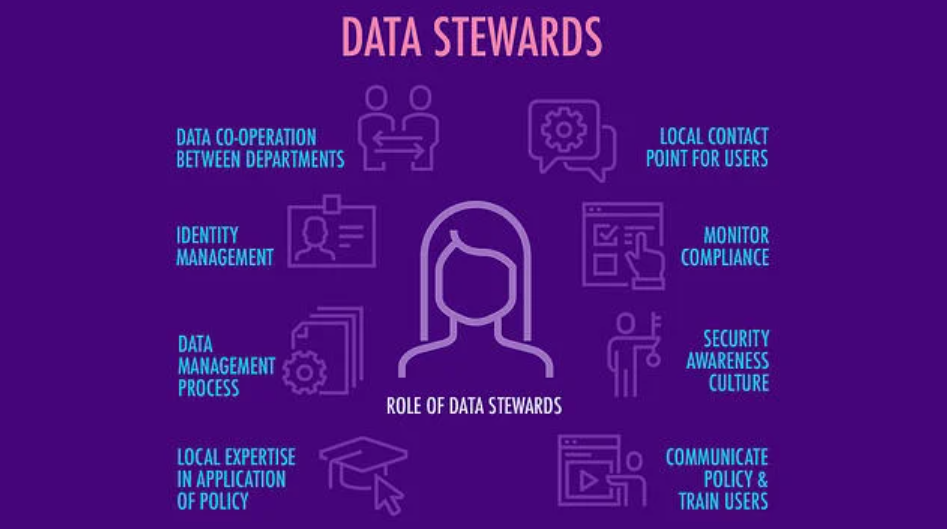
11. What is a data steward?
A data steward is an individual responsible for the day-to-day management of one or more datasets. They report to the data owner and work to maintain the security and quality of the data. Data stewards may or may not have any decision-making authority over their data.
Frequently Asked Questions in Data Governance
12. What is the difference between a data owner and a data steward?
Data owners are formally responsible for the quality of one or more datasets, while data stewards are responsible for the day-to-day management of the datasets themselves. In some organizations, the responsibilities of both roles will be performed by the same person. Larger organizations will assign these roles to multiple individuals to facilitate oversight and accountability, reduce the workload of senior staff, and encourage IT and business participation in data governance.
13. What is data quality and how is it measured?
Data quality deals with whether a particular dataset is fit for purpose. In other words, data that can be used to achieve specific business goals is considered high quality. DAMA measures data quality from 6 key dimensions: accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, validity, and uniqueness.
14. What is data management maturity and how do you measure it?
Data management maturity refers to a company’s ability to collect, manage, and monetize data. Data management maturity focuses on an organization’s ability to utilize and manage data, not the quality of the data itself. Measuring data management maturity need not be a complex process. It requires looking at many different organizational practices and data touchpoints.
15. What is data lineage?
Data lineage processing tracks the complete life cycle of a particular dataset or element: where it comes from, where it is converted or stored, and how it is ultimately used. Data lineage is particularly useful for determining the confidence of data and for analyzing the impact and root cause of data errors.

Frequently Asked Questions in Data Governance
16. What is a business glossary?
A business glossary defines the meaning, format, and purpose of an organization’s key data elements. A business glossary is critical to keeping everyone on the same page. By contextualizing and defining individual data elements, they improve business understanding, save time searching for reports, and prevent misuse. Business glossaries encourage better data-driven decision-making and are an important part of data governance.
17. What is the difference between a business glossary and a data dictionary?
A business glossary defines and contextualizes key data and reporting elements for the entire organization. They are written in easy-to-understand plain text, and terms are often cross-referenced for clarity. In contrast, a data dictionary is a table or set of tables that serves as a centralized repository for technical metadata. Data dictionaries are rarely used outside of IT.
18. How to build a business glossary?
The first step in building a business vocabulary is to map key business processes. Make sure to document and define every data element, business term, KPI and metric used in the process. Includes definitions of how data elements are formatted, who is managed, and where they are stored.
19. How to prioritize key data elements?
Critical Data Elements (CDEs) are data that directly advance corporate strategy and specific business goals. A great way to build a CDE is to map key business processes and identify which specific data elements are involved. Priority should also be given to data elements used in key reports within or outside the regulator.
20. When should you buy tools to help manage your data?
The people and processes for developing a data governance program should be prioritized before investing in tools. Before you start buying software, it’s important to align data governance policies with company strategy, identify specific business goals, and define roles and responsibilities. Tools should only be seen as a means to enable employees to more effectively achieve their goals, not a way to ensure your participation in a data governance program.
Conclusion
That’s all for 20 frequently asked questions in data governance. If you have any questions about data governance, please leave a message to let us know. If you want to learn more about data governance, we would like to advise you to visit Gudu SQLFlow for more information.
As one of the best data lineage tools available on the market of 2022, Gudu SQLFlow can not only analyze SQL script files, obtain data lineage, and perform visual display, but also allow users to provide data lineage in CSV format and perform visual display. (Published by Ryan on Aug 6, 2022)
If you enjoy reading this, then, please explore our other articles below: